What Is Notching and Why It Matters in Procurement
What Is Notching?
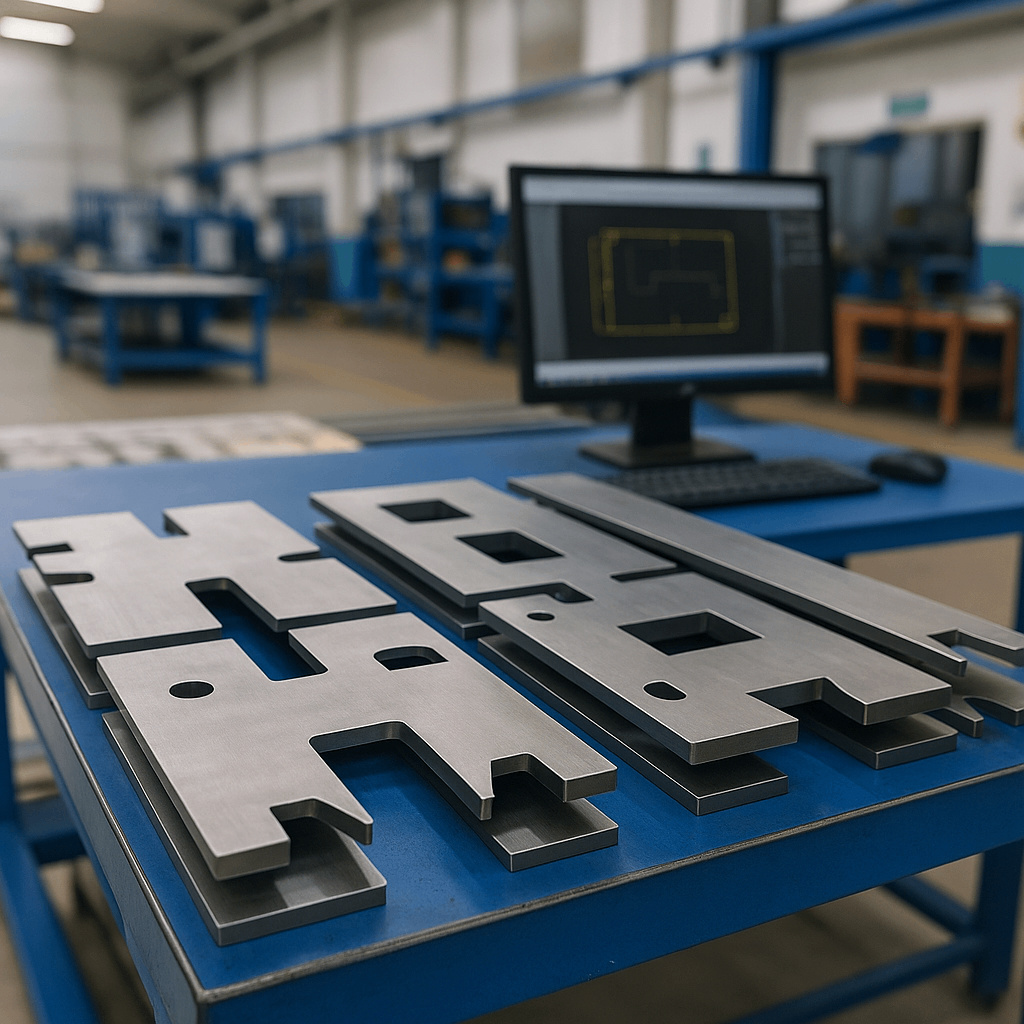
What is notching? It is a metalworking process used to cut predefined shapes from the edge or corner of a sheet metal part—typically applied before bending, forming, or welding.
Why It Matters to Procurement
For procurement professionals and wholesale buyers, notching plays a critical role in ensuring part fit, structural integrity, and tolerance accuracy. These factors directly influence production efficiency, minimize waste, and reduce rework—key priorities for scaling operations.
This guide examines how notching impacts manufacturing outcomes, cost control, and supplier selection. Whether sourcing custom metal cabinets or structural frames, understanding notching equips buyers to make informed decisions across OEM/ODM projects.
What Exactly Is Notching? A Practical Overview for Industrial Buyers
Notching involves removing small portions of sheet or formed metal to enable accurate bending, edge alignment, or joint integration. Unlike general cutting, it allows cleaner folds and distributes stress more evenly—ideal for enclosures, brackets, and welded frames.
Common materials include stainless steel (304/316), aluminum, galvanized steel, and cold-rolled steel. Each requires specific tooling and process control to prevent burrs, distortion, or cracking. For instance, aluminum notching challenges include edge deformation, often mitigated through controlled blade pressure and feed rate.
CNC notching delivers repeatable cuts with speed, while laser notching achieves tighter tolerances and handles complex geometries without mechanical wear.
Notching in Custom Manufacturing & OEM/ODM Projects
In OEM/ODM production, precision notching functions both as a fit-assurance mechanism and a means to uphold dimensional consistency. Poorly executed notches often lead to misalignments, weld defects, or secondary machining steps.
For example, an appliance manufacturer needed 0.2mm tolerance control on V-notches for door frames. Switching to a supplier offering laser notching and CAD-integrated prototyping reduced their assembly time by 18%.
Experienced suppliers like YISHANG support custom file formats (DXF, STEP, IGES) and provide engineering input to streamline notch geometry. This shortens sampling cycles and keeps projects on schedule.
With over 26 years of manufacturing experience and a global client base, YISHANG applies practical expertise to every project.
How Notching Enhances Efficiency and Product Quality
Material Optimization
Notching minimizes material waste by eliminating unnecessary overlaps and redundant cuts. Paired with smart nesting strategies, this enhances sheet utilization and reduces scrap—delivering material savings of up to 20% in some cases.

Assembly Speed and Accuracy
Precision notches act as built-in alignment guides during welding and assembly. This improves fit, shortens labor time, and lowers rejection rates—particularly valuable in automated welding environments where precision is essential.
Better Structural Reliability
Well-placed notches reduce stress concentrations that can lead to fatigue or cracks. For procurement teams, this means fewer warranty claims and greater confidence in long-term product durability.
Comparing Notching to Other Cutting Techniques
Metal cutting options include punching, blanking, shearing, and laser cutting. Unlike these, notching removes material selectively to enhance formability and downstream processing.
Blanking produces standalone parts. Shearing delivers straight-line cuts. Notching, by contrast, prepares corners or edges for folding, welding, or joining—making it ideal for components requiring precision assembly.
Understanding notching vs punching in sheet metal helps procurement teams choose the right approach for their part’s function, geometry, and integration process.
In complex builds, notching may also be combined with punch-laser techniques for increased flexibility.
Solving Real-World Challenges with Notching
Procurement professionals often face challenges like inconsistent tolerances, long tooling lead times, and incompatible notch profiles. High-precision notching addresses these by improving control and integration.
Case Study: Vending Equipment Supplier
A retail vending equipment client required tight corner fits on steel enclosures, but previous suppliers relied on mechanical cuts that introduced angle inconsistencies. Switching to laser notching via YISHANG reduced variance below 0.1mm and accelerated assembly by 25%.
Case Study: Solar Frame Manufacturing
An international energy supplier needed lightweight aluminum frames with rust resistance and field-assembly capability. YISHANG implemented custom radius notching and CNC tabs, removing the need for post-drilling and improving packing efficiency.
Notching for electrical cabinet manufacturing also enables precise wire routing and corner fitment—critical in electronics and control panel industries.
Integrating Notching Into Scalable Manufacturing
In volume manufacturing or multi-site programs, consistency is key. Notching must be embedded in a standardized workflow to avoid deviations in assembly or performance.
Automated CNC notching systems deliver uniform results, reducing reliance on manual intervention. For global procurement teams, this ensures stable quality and easier cross-factory replication.
Integration with upstream CAD data and downstream production tools creates closed-loop visibility. Whether managing enclosure fit or bracket precision, design-to-manufacture workflows reduce handoff errors and improve throughput.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What types of sheet metal are most suitable for notching?
Most sheet metals—including stainless steel (304/316), galvanized steel, aluminum, copper, and brass—can be effectively notched. Softer metals like aluminum may require precision tooling and pressure control to maintain edge definition and accuracy.
Q2: What is the standard tolerance for precision notching in industrial production?
With CNC or laser notching systems, industrial-grade operations can achieve tolerances as tight as ±0.1mm. This level of precision is critical in sectors like electronics, medical equipment, and control enclosures.
Q3: How does sheet metal notching differ from punching in fabrication processes?
Notching removes defined corner or edge sections to enable folding, fitting, or joining. Punching typically creates holes or large shapes within the sheet. Notching offers better control for high-precision assemblies.
Q4: Are custom notching services available for OEM or ODM parts?
Yes. Reputable suppliers like YISHANG provide custom notching based on 2D/3D drawings (e.g., DXF, STEP, IGES), including specialized angles, depths, and radii for specific part applications.
Q5: Which industries most commonly require precision notching services?
Key industries include electronics (e.g., electrical cabinet manufacturing), vending machines, medical devices, energy storage systems, automotive, and architectural metalwork. These sectors require exact component fit and consistent batch production.
Making Notching Part of a Strategic Procurement Plan
Notching is not just a fabrication step—it’s a strategic advantage in metal part procurement. For wholesale buyers, it affects fit, durability, and downstream efficiency. Understanding this process helps you select better suppliers, reduce production risks, and improve cost-performance balance.
Whether you’re sourcing welded cabinets, control enclosures, or structural assemblies, evaluating a supplier’s notching capabilities is essential. A capable partner like YISHANG can assist in CAD review, material selection, and efficient prototyping.


