The Unseen Risk — When a Handrail Project Fails Before It Begins
Most procurement failures in aluminum handrail systems aren’t due to faulty materials or underperforming surface finishes. They happen before the project even begins — during supplier selection.
For overseas buyers, particularly those sourcing from China, it’s tempting to make decisions based solely on price quotes, catalogs, or brochure-style websites. But when aluminum handrail parts are treated as off-the-shelf components rather than part of an engineered system, the risk of post-installation issues multiplies.
Misalignment of joints, tolerance stack-ups, improper finishing, and overlooked assembly constraints often lead to costly on-site adjustments, structural compromise, or even system-wide failure. In large-scale commercial or hospitality projects, these errors translate into shipment delays, safety concerns, and reputational damage.
Why Traditional Sourcing Logic Doesn’t Work for Modular Railing Systems
The Pitfall of Checklist-Based Procurement
Buyers often issue RFQs with predefined checklists: 6063-T5 aluminum, anodized silver, brushed finish, M8 fixing threads. On paper, these specs seem sufficient. In practice, however, they ignore the system-wide interdependency of railing components.
A railing bracket with ±0.2mm tolerance might pass QA individually — but when paired with a mounting base that’s off by 0.3mm, the assembly can distort. In modular systems, this cumulative error introduces visible misalignment, especially on long runs or when multiple kits are joined on-site.
Fragmented Sourcing = Hidden Risk
Some buyers attempt to optimize costs by sourcing handrail tubes from one supplier, fittings from another, and wall brackets from a third. While this might reduce unit pricing, it creates compatibility gaps and QA blind spots.
No single supplier is accountable for end-fit, load-bearing integrity, or anodizing uniformity. Worse, different batches from different plants often vary in alloy purity, extrusion consistency, and even color tone — a disaster for projects that demand visual and structural uniformity.
Engineering Challenges in Manufacturing Aluminum Handrail Parts
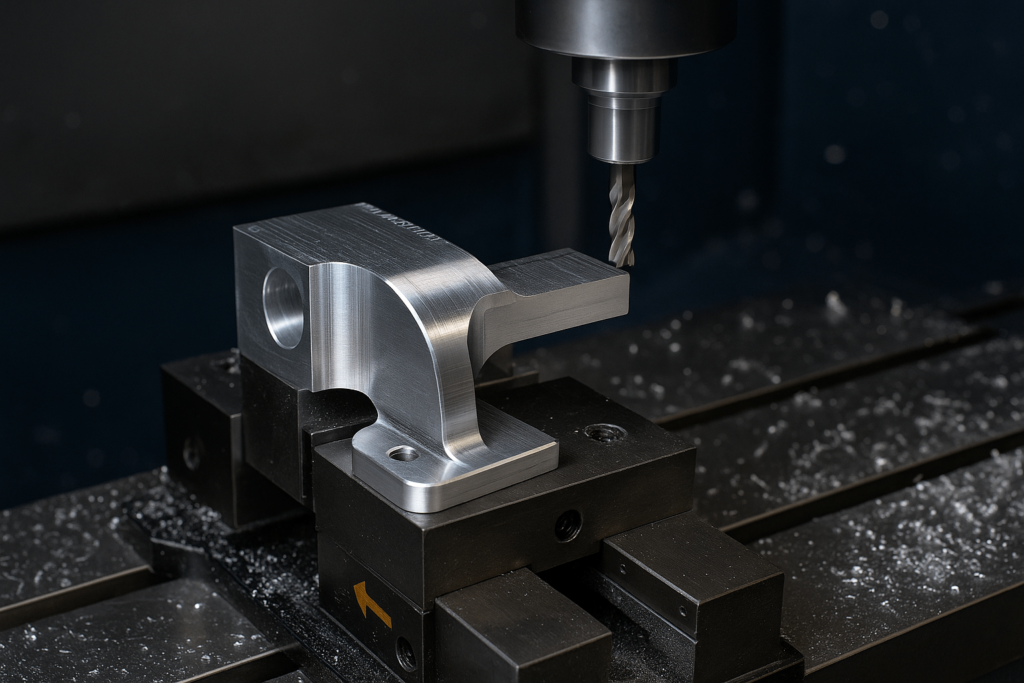
Precision Machining for Assembly Compatibility
Tolerance control is a non-negotiable in handrail part production. Components like elbows, wall returns, brackets, and connectors must meet positional tolerance specs within ±0.05mm to allow seamless fitment.
Milling grooves, hole positioning for screw channels, and angular cuts (typically 30°, 45°, 90°) require multi-axis CNC machining, often with fixture jig support to avoid shift during drilling. Additionally, pre-anodizing deburring is crucial to prevent finish chipping during field assembly.

Finish Control: Beyond Visual Appeal
While brushed, matte, or glossy anodized finishes are typically specified for aesthetics, their real engineering value lies in corrosion resistance, color uniformity, and grip functionality.
A well-controlled anodizing process should maintain ΔE* (color deviation) under 2.0 between parts. Gloss Units (GU) are typically held within ±5 across multiple batches. Surface hardness (Vickers HV) for architectural-grade anodized parts ranges from 200–400HV, essential for scratch resistance and long-term durability.
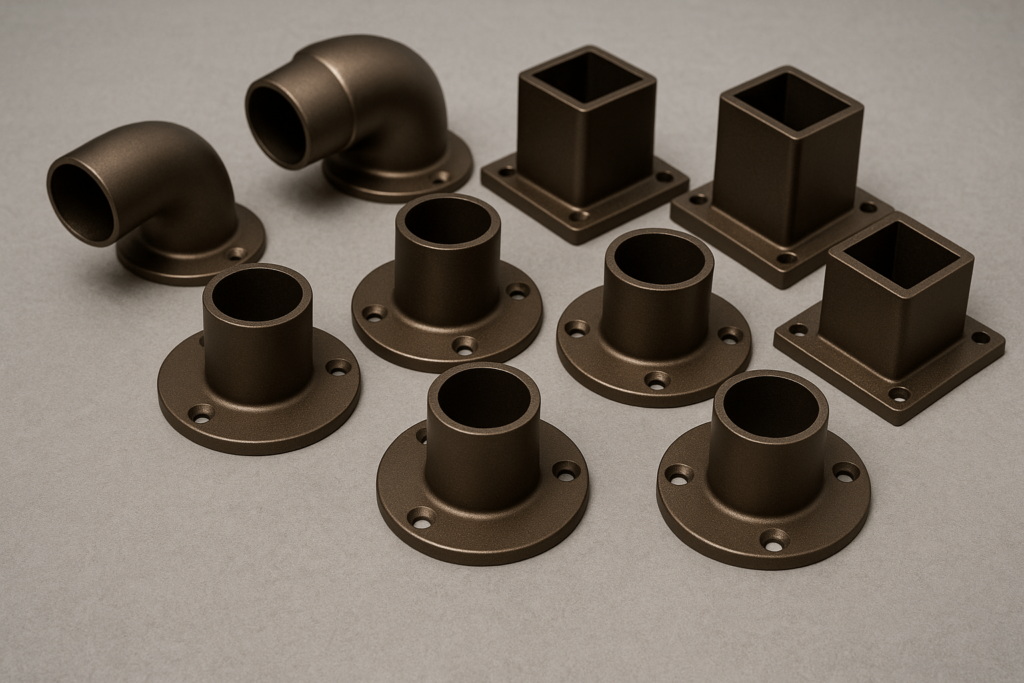
Structural Strength, Wall Thickness, and Safety Factors
Buyers often overlook the importance of uniform wall thickness (e.g., 2.0mm ±0.1mm) in load-bearing parts such as vertical posts and mounting flanges. Uneven extrusion or poor alloy mixing leads to stress concentration, which can trigger premature failure under shear or torsion.
Third-party suppliers should be able to provide mechanical property sheets (yield strength, elongation, hardness) based on batch-level testing — especially if the handrail system is used in high-traffic or public safety environments.
What Makes a Supplier “System-Ready” vs “Part-Only”
System Simulation & Mock Assembly
An engineering-qualified supplier should perform mock assembly validation before mass production. This includes simulating full segment assemblies (e.g., 2m rail section with 3 brackets) using jigs to test fitment and straightness.
They should offer simulation reports that highlight:
- Misfit incidence rate
- Assembly time per unit
- Deviation between theoretical and actual angular alignment

Documented Tolerances and Traceability
True system-level suppliers provide a quality assurance matrix with CPK (Process Capability Index) values, traceable back to individual production batches. These documents help procurement managers correlate defects to production anomalies.
Key QA parameters include:
- Bore and hole positions (±0.05mm)
- Wall flatness (≤0.1mm warp per 300mm length)
- Anodizing thickness (10–15μm architectural standard)
ECN (Engineering Change Notification) Control
Changes in extrusion die, finishing process, or even packaging layout can affect final assembly. Suppliers must maintain ECN logs that track all design or process modifications. This ensures repeat orders remain dimensionally consistent across procurement cycles.
Case Study — How 1mm Error Delayed a Hospitality Project by 2 Weeks
A UK-based contractor sourced wall flanges, brackets, and railing tubes from three different Chinese suppliers. While each part passed their individual QA inspections, field installation revealed a consistent 1.2mm misalignment across 180 bracket mountings.
The result? Re-drilling anchor holes on-site, extra labor, overnight reshipments of corrected parts, and two weeks of project delay. Total loss: over $15,000 in unplanned expenses. All could have been avoided by sourcing from a system-ready supplier that performs mock assembly and maintains cross-batch dimensional control.
What to Include in Your RFQ to Ensure Manufacturability
Drawings That Go Beyond Shape: What Engineers Should Send
Instead of generic CADs, engineers should submit technical drawings that include:
- GD&T symbols (true position, flatness, perpendicularity)
- Critical-to-fit dimensions with tolerance ranges
- Surface finish callouts (Ra, GU, ΔE*)
- Exploded assembly reference views
This enables suppliers to pre-empt fitment issues and suggest cost-saving alternatives (e.g., switching from threaded to slot-joint connection if tolerance is tight).
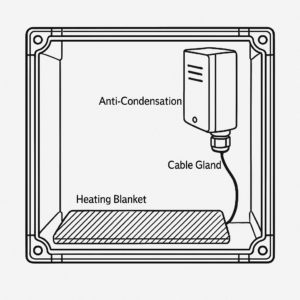
Thermal and Condensation Management
For outdoor railing projects in humid or coastal climates, condensation buildup inside handrail tubes can trigger premature corrosion or freeze-expansion failures. Suppliers should offer solutions such as:
- Drainage holes at defined intervals
- Anti-condensation plugs or vents
- Integrated heating film options for cold-weather installations
Evaluating Supplier Capability: A Quick Engineering Checklist
Use this 5-point checklist when comparing Chinese aluminum handrail suppliers:
- Can they simulate full assembly using actual parts?
- Do they have in-house CNC, extrusion, and anodizing?
- Can they provide batch-specific tolerance reports?
- Is their documentation ECN-controlled?
- Are their surface finish specs backed by measurable data (GU, HV, μm)?
Final Thoughts — Don’t Just Source Parts. Source Systems.
Aluminum handrail systems are more than tubes and brackets. They are load-bearing, safety-critical assemblies that require integrated design, dimensional compatibility, and finish control.
[Appendix] Key Tolerance & QA Benchmarks for Sourcing
| Parameter | Typical Spec | Measurement Method |
|---|---|---|
| Bore Diameter Tolerance | ±0.05mm | Digital Caliper |
| Angular Deviation | ≤0.3° | CMM |
| Anodizing Thickness | 10–15μm | Eddy Current Tester |
| Surface Gloss Deviation (GU) | ≤ ±5 | Glossmeter |
| Wall Thickness Variation | ≤0.1mm | Ultrasonic Thickness Gauge |
Frequently Asked Questions by Aluminum Railing Buyers
Q1: What alloy is most recommended for outdoor handrail systems?
A1: 6063-T5 is standard for architectural applications due to its corrosion resistance and good extrudability.
Q2: Can I order small batches for testing?
A2: Most suppliers have MOQ, but system-ready suppliers often offer small-batch prototyping if drawings are clear.
Q3: How do I ensure color matching across batches?
A3: Request color deviation control using ΔE* and gloss measurement between lots.
Q4: What should I check in their QA document before ordering?
A4: Focus on dimensional tolerances, surface thickness, and actual assembly records if possible.
Q5: Is FOB China the best shipping term for these parts?
A5: For bulk orders, FOB is preferred, but DDP or CIF can be arranged for clients unfamiliar with import logistics.

