Introduction: Beyond the 3D Model – A Strategic Approach to Enclosure Procurement
Your design is complete, and the 3D model looks perfect. Yet, a critical challenge remains: sourcing a custom aluminum enclosure that is durable, cost-effective, and flawlessly manufactured—especially when scaling from prototype to high-volume production.
This is where digital concepts meet the physical realities of metal. A single early mistake in alloy selection or a disregard for Design for Manufacturability (DFM) can trigger costly delays and budget overruns.
For a procurement manager, these are not just technical issues—they’re business risks that impact timelines and profitability. This guide is your strategic playbook for custom aluminum box fabrication, crafted to help navigate every critical decision point.
We’ll go beyond listing services to uncover the why behind each choice. This is the resource for turning your design into a tangible, high-performing product that strengthens your supply chain—whether you’re building a waterproof aluminum enclosure, an aluminum battery housing, or a machined aluminum electronics case.
Chapter 1: Choosing the Right Aluminum Alloy: The First—and Most Critical—Decision
The aluminum alloy you choose is the DNA of your custom aluminum enclosure. It governs everything from manufacturability to cost to long-term performance.
This decision shouldn’t rely on a single material property. Instead, let your fabrication method and application environment guide your choice—whether you’re planning a sheet metal aluminum box, CNC machined aluminum housing, or a waterproof aluminum project enclosure.
The "Big Three" Alloys: A Strategic Comparison
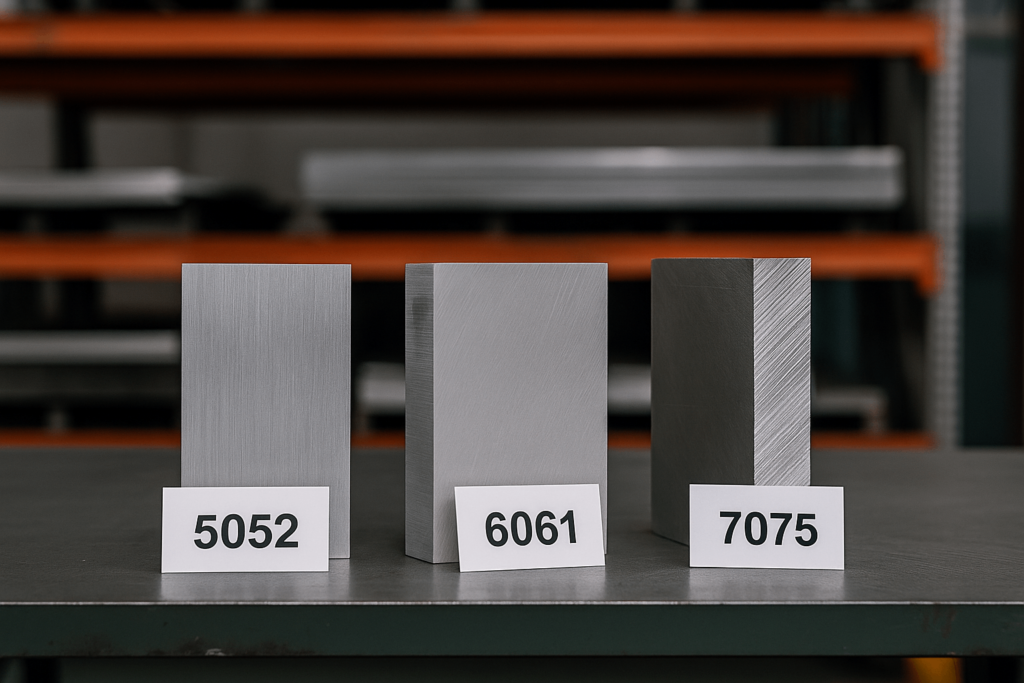

Among hundreds of aluminum grades, a few stand out as industry workhorses. These three alloys are foundational for predictable manufacturing outcomes in precision aluminum fabrication:
5052-H32: The Formable Workhorse. Magnesium-alloyed 5052 excels in sheet metal fabrication. The H32 temper indicates strain-hardening and stabilization. It bends easily without cracking, offering excellent corrosion resistance—ideal for welded or bent enclosures in harsh environments.
6061-T6: The Machinable All-Rounder. A heat-treated alloy with solid strength and weldability. The T6 temper provides optimal mechanical properties. It’s a go-to for custom aluminum boxes requiring CNC machined features thanks to its superior machinability.
7075-T6: The High-Strength Specialist. Primarily alloyed with zinc, 7075 is extremely strong—on par with some steels. It’s a staple in aerospace and motorsports, though its strength comes with reduced formability and weldability.
Data-Driven Material Selection
The following matrix supports procurement and engineering decisions with measurable comparisons:
| Property | 5052-H32 | 6061-T6 | 7075-T6 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength (Ultimate) | ~228 MPa | ~310 MPa | ~572 MPa |
| Yield Strength | ~193 MPa | ~276 MPa | ~503 MPa |
| Formability | Excellent | Good | Poor |
| Weldability | Excellent | Good | Fair/Poor |
| Machinability | Fair | Good | Fair |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent (Marine) | Good | Moderate |
| Anodizing Quality | Good | Excellent | Challenging |
Application-Based Alloy Selection
For bent sheet metal enclosures, 5052 is the most reliable and cost-effective.
For tapped holes and machined features, 6061-T6 ensures better thread quality and dimensional control.
For high-stress environments, like aerospace or heavy-load structures, 7075-T6 provides exceptional strength.
Avoid selecting alloys based on a single property. Always align your choice with intended form, function, and finishing. This approach is essential for durable, high-performance aluminum electrical enclosures and outdoor aluminum junction boxes.
Chapter 2: Design for Manufacturability—Transforming Ideas into Reality
A design that looks great but can’t be efficiently built is a liability. Design for Manufacturability (DFM) bridges the gap between idealized CAD and real-world production.
Essential DFM Principles for Sheet Metal
Follow these golden rules to avoid costly rework and ensure quality:
Bend Radii & Flange Lengths: Minimum internal bend radius = material thickness. Flange lengths should be ≥ 4× material thickness.
Hole Placement: Keep holes at least 4× thickness away from bend lines to avoid distortion.
Standardization: Use standard hole sizes and uniform radii wherever possible to leverage existing tooling and reduce cost.
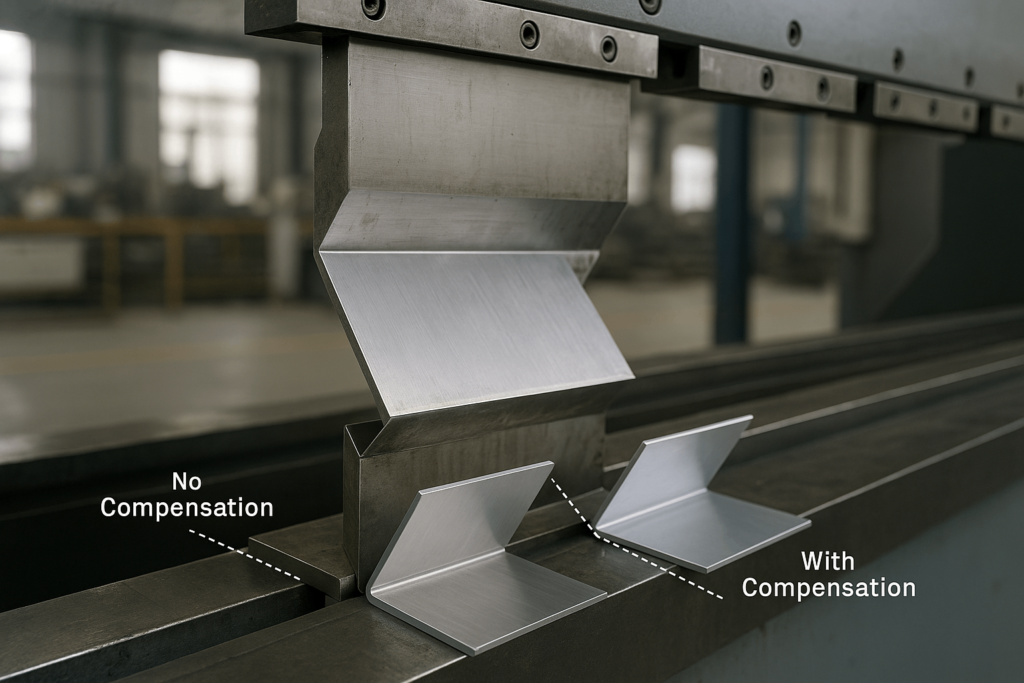
Springback: Predicting and Controlling Aluminum’s Elastic Return
Aluminum naturally springs back after bending due to elastic recovery. Compared to steel, its springback is more pronounced.
Fabricators counteract this with:
Overbending to compensate for elastic return.
Sensor-driven CNC press brakes that adjust in real time for consistent angles.
Chapter 3: Inside the Fabrication Workflow
From digital model to physical product—this is the journey of custom aluminum fabrication for enclosures, housings, brackets, and structural shells.
Step 1: Cutting – Laser vs. Turret Punching
Laser Cutting: High precision and flexibility, best for low-volume or complex geometries.
Turret Punching: Fast and efficient for repetitive standard features in high volumes.
Step 2: Forming with the Press Brake
The press brake bends flat blanks into 3D forms using matched punches and dies. Stroke depth and tooling geometry determine accuracy.
Step 3: Joining – Optimize for Performance and Cost
Joining method depends on enclosure size, function, and volume:
TIG Welding with AC handles aluminum’s oxide layer effectively but requires skill and introduces heat.
Mechanical Fasteners (e.g., PEM®) are ideal for repeatability, speed, and minimizing thermal stress.
For high-volume custom aluminum box fabrication, fasteners often outperform welding in precision, efficiency, and EMI performance. Choose joining methods based on lifecycle performance and enclosure requirements—especially for aluminum electronics enclosures or communication device housings.

Chapter 4: Surface Finishing Options
The right surface finish enhances function, protection, and appearance.
Anodizing
Type II: For aesthetics and corrosion resistance.
Type III (Hardcoat): For wear and abrasion resistance.
Powder Coating
Electrostatically applied and cured. Offers robust color finishes and strong environmental resistance. Popular for industrial control boxes and heavy-use aluminum chassis.
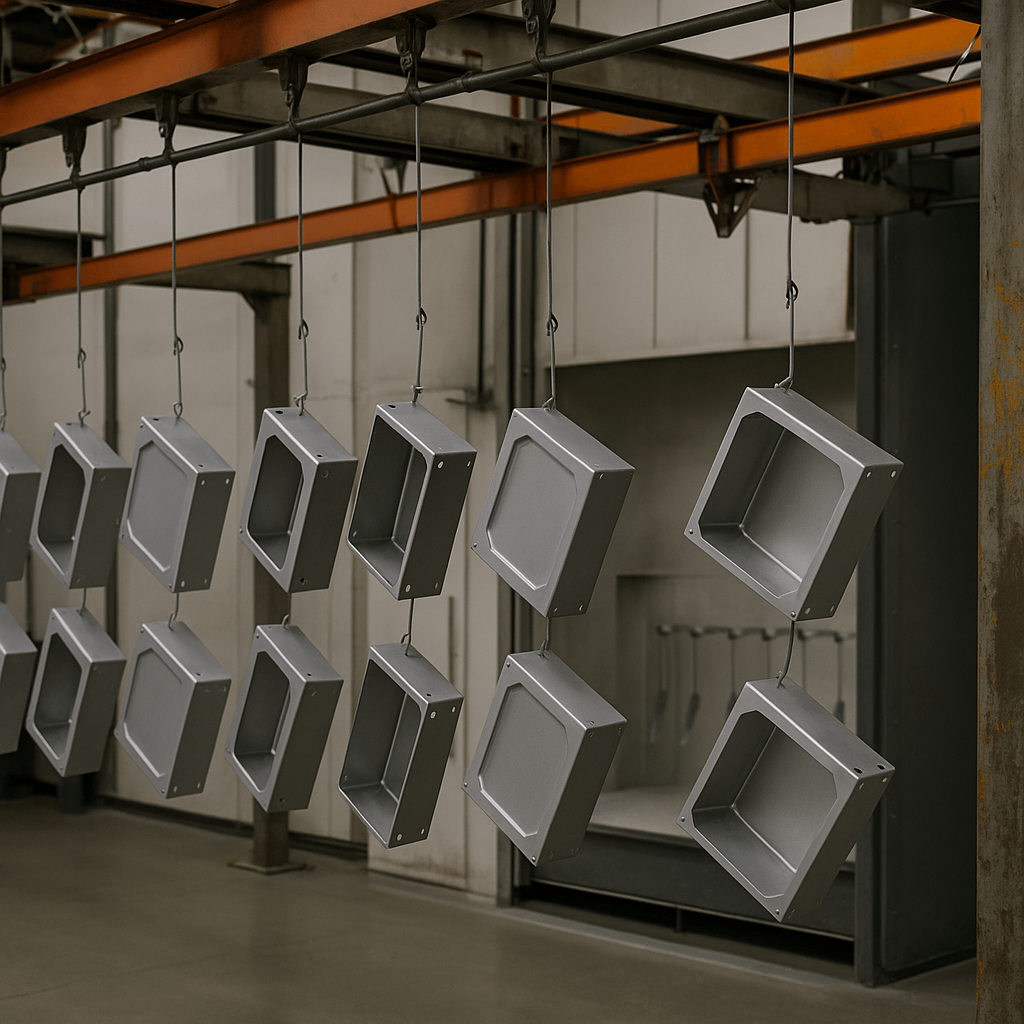

Chem Film (Alodine)
Allows conductivity while offering corrosion protection. Ideal for EMI-sensitive applications such as RF enclosures and telecom boxes.
Consider Finishing Tolerances Early
Surface treatments add measurable thickness. Type III can add ~0.002 inches. Specify finishes during design to prevent downstream interference.
Chapter 5: Engineering Enclosures for Harsh Environments
Ingress Protection (IP) and NEMA Ratings
IP67: Dust-tight and immersion-resistant.
NEMA 4X: Adds corrosion resistance.
Achieving these involves:
Flat, rigid mating surfaces.
Uniform fastener torque.
Quality gaskets (often silicone).
EMI/RFI Shielding
Aluminum acts as a Faraday cage—but only if seams maintain electrical continuity. Use conductive gaskets to prevent leakage.
Waterproofing vs. EMI Dilemma
Silicone gaskets seal well but block conductivity. Conductive gaskets conduct but may not seal water. Hybrid gasket solutions are often necessary.
For waterproof aluminum enclosures that also require EMI shielding, proper gasket selection and joint design are critical to maintain both electrical integrity and environmental sealing.

Chapter 6: Choosing the Right Fabrication Partner
Execution is everything. Beyond low pricing, evaluate your vendor’s capability, quality systems, and communication.
Beyond Visual Checks
Serious QA includes:
Dimensional Verification (calipers, CMMs)
First Article Inspection (FAI)
Documentation & process control
Five Questions to Vet Your Fabricator
Do they provide DFM feedback proactively?
What processes are in-house?
Have they built similar parts before?
Are they ISO 9001 certified?
Is communication structured and consistent?
Conclusion: Turnkey Execution Starts with Smart Fabrication
From alloy choice to finish, from bend to seal—every decision affects performance and manufacturability. Success means working with a vendor who sees beyond specs.
At YISHANG, we bring over 26 years of fabrication experience, in-house capabilities from laser cutting to finishing, and a team that partners with you—not just quotes your print.

