Introduction
Metal casting is the act of pouring molten alloy into a pre-shaped mold, letting it solidify, and then extracting the finished part. Though the basic principle is ancient, modern foundries combine automation, advanced mold materials and rigorous QC to support everything from automotive engine blocks to precision aerospace components.
What Is Metal Casting – Overview for Procurement & Manufacturing
Casting is a manufacturing process where molten material is poured into a mold and allowed to solidify into the desired shape. It is a widely used method for creating complex parts, such as engine blocks, turbine blades, and automotive components. For wholesale buyers, understanding molding techniques is crucial for making cost-effective procurement decisions, choosing the most efficient method based on production needs.
Why Casting Matters for Wholesale Buyers
Cost Efficiency: Molding and casting methods allow for large-scale production at a reduced cost per unit, making them ideal for bulk procurement.
Customization: Whether you need abrasion-resistant investment cast parts or custom aluminum moldings, this technique offers flexibility in both design and material selection.
Material Versatility: These methods accommodate a wide variety of materials, from aluminium die-cast components to alloyed cast iron, providing flexibility to meet diverse product specifications.
Time Savings: Faster production methods like die-casting and permanent mold casting allow for quick turnarounds, critical for maintaining tight delivery schedules.
Bevels are especially beneficial for industries requiring high-strength joints or customized designs, particularly for small-volume production or custom orders.
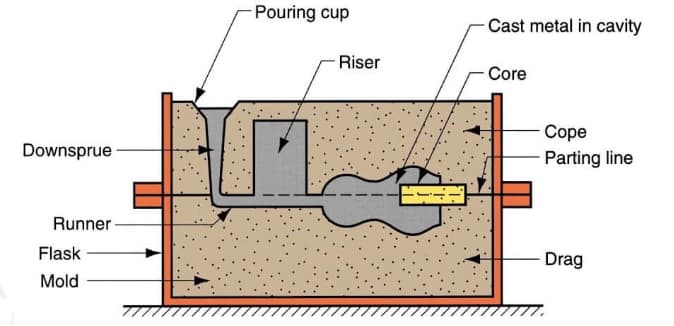
Major Casting Methods at a Glance
Understanding the various molding techniques is crucial for selecting the right one for your production needs. Below, we break down each process and its most relevant benefits for wholesale procurement:
1. Sand Casting – Cost-Effective, Flexible for Large Parts
Ideal for: Large parts such as engine blocks and industrial components.
Advantages: Low initial mold costs, flexible for large parts and low to medium-volume production.
Limitations: Rougher surface finish and lower precision compared to other methods.
Best for: Large, simple parts where cost efficiency is the priority. Typically used in large-scale industrial applications.
2. Investment Casting (Lost-Wax) – Precision & Complex Shapes
Ideal for: Aerospace components, medical devices, and high-precision parts.
Advantages: High precision, excellent surface finish, and minimal material waste. Perfect for intricate designs.
Limitations: Higher production costs and slower cycle times due to its multi-step process.
Best for: Low to medium-volume production requiring complex designs and high precision, often used in industries like aerospace and medical devices.
3. Die Casting – High-Volume, Fast Turn-Around
Ideal for: Aluminium die-cast products used in automotive, electronics, and consumer goods.
Advantages: High precision, fast production speed, and smooth finish. Ideal for mass production.
Limitations: High initial mold costs, best suited for non-ferrous metals such as aluminium and zinc.
Best for: High-volume production runs that require precision and fast turnaround.
4. Permanent Mold Casting – Mid-to-High Volume with Reusable Molds
Ideal for: Aluminium die-casting for medium to high-volume production.
Advantages: Better dimensional accuracy and smoother finishes compared to sand molding.
Limitations: Limited to simpler shapes, lower volume runs compared to die molding.
Best for: Medium to high-volume production where consistency and quality are required, such as in aluminium components for industrial machinery.
5.Shell Moulding – A Hybrid Between Sand and Investment Moulds
Shell moulding uses a resin-coated sand “shell” around a heated metal pattern to form a moulding cavity. It delivers finer surface finish compared to traditional sand casting and supports moderate-volume production of complex parts with internal undercuts. This method bridges the gap when investment casting is too costly and simple sand casting lacks the required tolerances.
| Process | Typical Production Volume | Typical Materials | Key Strengths | Typical Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sand Casting | Low to Medium (few to thousands) | Steel, iron, aluminium | Low tooling cost, large parts | Lower precision, rougher surface |
| Investment Casting | Low to Medium | Stainless, superalloys | High precision, thin walls | Higher tooling cost, slower cycle |
| Die Casting | Medium to High | Aluminium, zinc, magnesium | High throughput, excellent surface finish | High initial die cost, limited to non-ferrous |
| Permanent Mold Casting | Medium to High | Aluminium, magnesium | Reusable moulds, good dimensional control | Mold cost still significant, shape complexity constrained |
| Shell Moulding | Medium | Steel, iron | Better surface finish than standard sand | Tooling and shell cost higher than sand |
How to Choose the Right Casting Process for Your Needs
When selecting the most suitable molding process, wholesale buyers should evaluate several key factors to ensure that the process aligns with their production goals:
Material Compatibility: Each molding technique is best suited for specific materials. For example, aluminium die casting is ideal for lightweight, durable parts, while alloyed die casting works best for high-strength applications.
Production Volume: Die molding and permanent mold molding excel in high-volume production, while investment molding is better suited for low to medium-volume, high-precision parts.
Cost and Lead Time: Sand molding is a low-cost option for small batches, whereas die molding provides faster production for larger runs, making it ideal for time-sensitive orders.
Precision and Finish: If your parts require high precision or a smooth finish, investment molding and die molding should be your choice.
How to Select the Best Casting Process – A Step-by-Step Framework
Step 1 – Define annual quantity and batch size.
Step 2 – Confirm alloy type and finish requirements.
Step 3 – Compare total cost including tooling amortization and lead time.
Step 4 – Review supplier quality systems and defect-control methods.
Step 5 – Assess production flexibility and logistics to your target markets (US / Europe).
Step 6 – Choose the process offering the lowest total landed cost for your expected demand.
Casting Process Defects & Mitigation
At YISHANG, we prioritize quality by using advanced techniques to minimize common defects and ensure the best possible product:
Porosity: Caused by trapped gas in the molten material. We prevent this with advanced degassing techniques, ensuring a uniform and solid product.
Shrinkage: Occurs when molten metal cools and contracts. We optimize gating systems to minimize shrinkage and ensure complete filling of the mold.
Inclusions: Foreign materials trapped in the molding can weaken the part. We follow strict quality control measures to guarantee that our materials are clean and free of contaminants.
For example, during aluminium wheel hub production, trapped gas can lead to porosity and weaken the part’s structure. By applying vacuum-assisted degassing and controlled mold temperature, manufacturers can reduce internal cavities and guarantee consistent density. This approach ensures fewer rejects and higher reliability for automotive suppliers.
FAQ
1. What is the best manufacturing process for high-volume production?
For high-volume production, die molding is often the best choice. It offers rapid production with high precision. Permanent mold molding is another excellent option for medium to high-volume production of simpler parts.
2. What are the advantages of investment molding?
Investment molding provides high precision, excellent finish, and minimal material waste. It is ideal for parts with intricate designs, often used in aerospace, medical devices, and other high-precision industries. While the initial costs are higher, the quality and precision justify the investment for low to medium-volume production.
3. How do I choose the right molding process for my product?
Choosing the right molding process depends on:
Material compatibility: Different processes work best with certain materials.
Precision and finish: If high precision and smooth finishes are required, investment molding or die molding may be the best option.
Production volume: For high-volume runs, die molding and permanent mold molding are more efficient, while investment molding is ideal for low to medium volumes.
Cost considerations: Ensure that the process chosen balances long-term cost savings with the required production speed and quality.
4. What materials can be used in molding?
Molding processes are compatible with a variety of materials, including:
Aluminium alloys: Commonly used in aluminium die casting for lightweight, durable parts.
Alloyed cast iron: Ideal for applications that require high strength and durability.
Steel: Often used in investment molding for high-strength parts.
Brass and bronze: Commonly used for parts requiring corrosion resistance and aesthetic finishes.
5. How does molding impact lead times?
Lead times can vary based on the molding process:
Die molding provides the fastest production speed, making it ideal for large orders with tight deadlines.
Investment molding typically takes longer due to its multi-step process, but it is ideal for parts requiring high precision.
Sand molding is slower and less efficient for large orders but is cost-effective for small production runs.
6. What role does quality control play in molding?
Quality control is essential to ensure the final product meets all required specifications. Common methods include:
Visual inspections: Checking for defects like cracks, surface imperfections, and porosity.
Dimensional testing: Ensuring the part meets the required tolerances.
Non-destructive testing (NDT): Methods like ultrasonic testing to detect internal defects without damaging the part.
7. Can YISHANG handle large-scale orders?
Yes, YISHANG specializes in both small batch and large-scale orders. Our die molding and permanent mold molding processes are ideal for high-volume production runs, ensuring you receive high-quality parts at competitive prices, even for large orders.
8.What is the minimum order volume that makes die casting cost-effective?
Die casting becomes cost-efficient when annual production exceeds roughly 5,000 units. Below that volume, methods like shell or investment casting are more economical.
9. Can recycled aluminium alloys be used in casting?
Yes. Recycled aluminium can perform well if controlled for impurities. Reputable foundries test the chemical composition to ensure consistent mechanical strength.
10. How can buyers compare quotes across different casting suppliers?
Always check whether the quotation includes tooling amortization, scrap rate, and testing costs. The lowest unit price may not equal the lowest total cost once logistics and quality factors are considered.
Conclusion
Selecting the ideal casting process is not just about technical compatibility—it’s about long-term value. At Yishang, we specialise in aluminium die castings, permanent-mold solutions, and precision investment castings tailored to meet demanding global standards. Whether you require short runs or large-scale orders, our engineering team and quality assurance systems deliver consistent, cost-effective results to customers in the US and Europe.
Ready to optimize your procurement process with reliable molding solutions? Contact YISHANG today to discuss your specific needs and learn how we can provide tailored solutions to meet your business requirements.

